The Critical Nature of High-Performance Security in the Age of Edge Computing
As of April 2021, it was reported that over 30 percent of survey participating organizations were running more than 50 percent of workloads in the cloud. Furthermore, in the next 12 to 18 months, it is expected that 56 percent of organizations will run above 50 percent of workloads in the cloud. These statistics should come as no surprise. But how about edge computing? The global edge computing market was valued at USD 4.68 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 250.6 billion by 2024. While cloud computing is no longer a new concept for enterprises, there is more adoption of edge computing given the rise of 5G and Internet of Things (IoT).
Now, edge and cloud computing are entwined in our lives, and will continue to be. This fast-changing environment leads to question of security. Before we get into that, let’s take a closer look at what exactly edge computing is, what the positive impact of edge computing has on businesses, and how the edge and cloud coexist.
What exactly is Edge Computing?
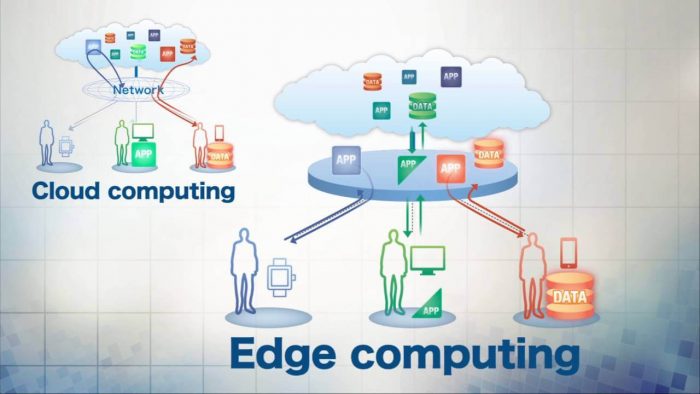
It is important to note that edge computing and cloud computing are different. Edge computing is to the relocation of processing functions closer to users or devices (the “edge” of the network). Since data can be processed at the edge, edge computing networks can greatly reduce latency and enhance performance. On the other hand, cloud computing is the delivery of services through the internet (Cloud). Services include but are not limited to servers, storage, and software.
Benefits of Edge Computing for Businesses
We know what the differences are now, but what about their impacts on businesses? Edge computing has four main benefits for businesses: reduction of latency, real-time data analysis, scalability, and reliability.
Saving Bandwidth
Using traditional cloud computing frameworks lead to large amounts of data accumulation. With edge computing, the critical data is sorted out while other data deemed unimportant can be sorted and sent to the cloud for further analysis later. As collected data does not need to travel back to a central server for a device to execute a function, businesses can save operational costs and their data storage.
Reduced Latency
Speed is undeniably vital for any business or organization. It may not matter so much for individual users using Siri and Alexa to have slight delays to questions about the weather, but that is certainly not the case for businesses. Especially, slight delays could be a matter of life or death to businesses in the industries of related to healthcare or autonomous car. With edge computing, only vital data that helps to make imminent decisions can be processed on the spot, allowing for faster response times.
Real-time Data Analysis
Since edge computing drives computing as close to the source of data generation as possible, businesses can process the most relevant data for them in real-time to make faster and better decisions. These decisions can make a significant impact on a businesses’ operations and profitability. For example, in smart manufacturing, the near-immediate analysis on the manufacturing floor allows the business to improve operational efficiency and increase their bottom line.
Scalability
Traditional IT infrastructures (such as data centers) tend to hinder the growth of businesses as it forces them to anticipate their needs ahead of time. Not only is it a large up-front cost, but there is also maintenance cost to worry about. However, edge computing and cloud-based technology has business scalability. Traditional IT infrastructure capabilities are able to fit into devices with smaller footprints and placed closer to end-users. Expanding a business no longer requires centralized data centers, instead colocation services with edge computing data centers across regions can help businesses expand their network much quicker and cost-effectively.
Reliability
Reliability in the context of edge computing is deeply connected to the previously mentioned benefits above. For example, with IoT edge computing devices, since edge data centers are nearer to end-users, it lowers the probability of distant network problems affecting local users. Even if outages happen in the vicinity, the native vital processing functions allow edge computing devices to continue operating effectively. The sheer number of edge computing devices and data centers connected to the network prevents any singular failure to complete shutdown.
Need for High Performance Security Management
Unlike traditional cloud computing that has its vulnerability to distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks and power outages, edge computing distributes processing functions across a wide range of devices. This makes it difficult for single disruptions to completely shut down a network. However, a major security concern is that given the large number of edge computing devices, each one could be used as a point of entry for cyberattacks. This means malware and other intrusions could infect a network from any single weak point. While that is true, the implementation of security measures is much easier, and each compromised device can be dealt without shutting down an entire network.
If you’re wondering how to start protecting your business with edge and/or cloud computing from cyber-attacks, Cloudbric is a great place to start. Cloudbric provides affordable fully managed security services including web, managed and custom services. To learn more about security software offerings or get started, simply fill out the form here.